Evolving the GRC Role in the AI Era: NIST AI RMF
June 27, 2024
In our rapidly advancing technological landscape, integrating artificial intelligence (AI) systems has become ubiquitous across various industries, revolutionizing business operations and processes. As organizations harness the power of AI to drive innovation and improve efficiencies, the role of Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) professionals is evolving to address the unique challenges posed by AI adoption. This article delves into the critical aspects of managing risks and ensuring trustworthiness in the AI era, highlighting the new responsibilities and characteristics that define the modern GRC role in artificial intelligence. AI poses many risks that organizations must navigate, ranging from algorithmic biases and data privacy concerns to cybersecurity threats and regulatory compliance issues. GRC professionals now find themselves at the forefront of developing strategies to mitigate these risks effectively while fostering a culture of responsible AI use within their organizations.
The traditional GRC framework is being reshaped to encompass the complexities of AI governance. It requires a deep understanding of AI technologies, their ethical implications, and the legal frameworks that govern their deployment.
To effectively manage AI socio-technology risks, organizations can find value in implementing established frameworks such as NIST AI RMF, offering structured guidelines for enhancing GRC practices in this dynamic landscape.
Impacts of AI Risks:
The advent of Artificial Intelligence has reshaped the risk landscape, broadening the scope to encompass potential harm not only to organizations but also to individuals, communities, and the environment. Distinguishing AI technology risks from traditional technology risks is crucial due to the varied nature of AI-related impacts and harms. This differentiation calls for a nuanced risk management approach at every stage of the AI lifecycle.

Trustworthiness in AI Systems:
The measurement of AI risk mandates a holistic approach, which includes defining roles, engaging stakeholders, and evaluating trustworthiness from social and organizational viewpoints. Trustworthiness in AI systems embodies critical traits such as validity, reliability, safety, security, accountability, transparency, explainability, privacy improvement, and fairness in combating detrimental biases. Ensuring these characteristics are embedded within AI systems fosters trust among users, regulators, and the larger community, underscoring responsible and ethical AI deployment.
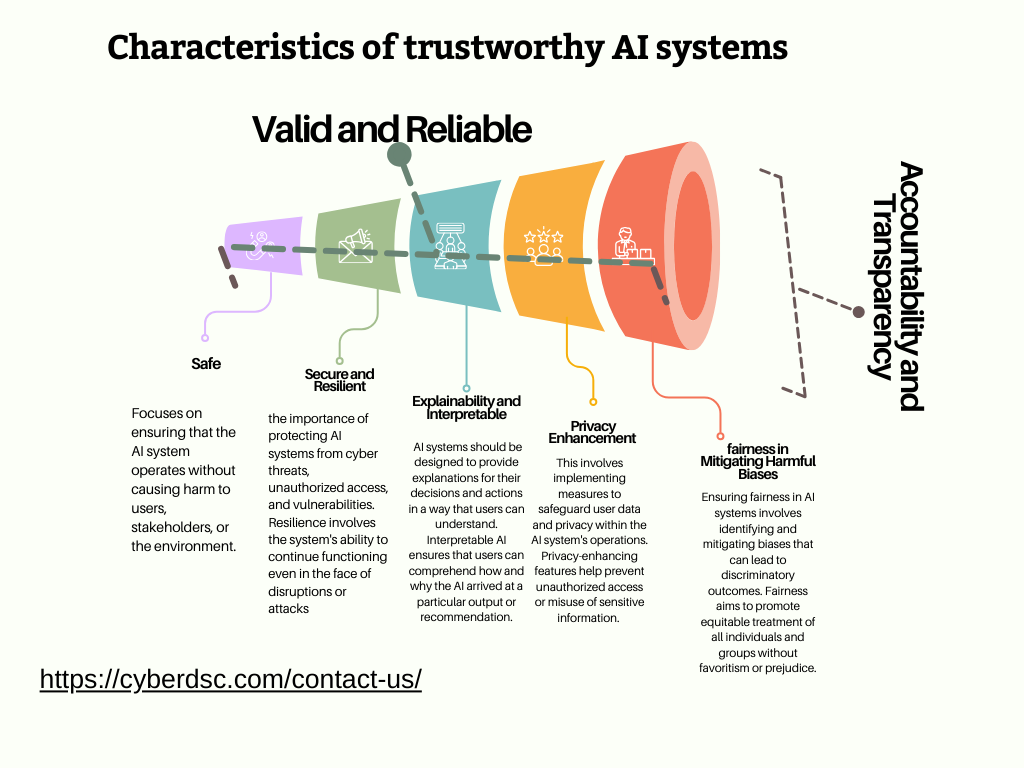
The characteristics related to trustworthiness in AI systems:
Safe: A “safe” AI system operates in a manner that minimizes risks to users, data, and the environment. It involves ensuring that the AI system performs its functions without causing harm, injury, or damage.
Secure and Resilient: This characteristic emphasizes the importance of protecting AI systems from cyber threats, unauthorized access, and vulnerabilities. Resilience involves the system’s ability to continue functioning even in the face of disruptions or attacks. 3. Explainability and Interpretable: AI systems should be designed to provide explanations for their decisions and actions in a way that users can understand. Interpretable AI ensures that users can comprehend how and why the AI arrived at a particular output or recommendation.
Privacy Enhancement involves implementing measures to safeguard user data and privacy within the AI system’s operations. Privacy-enhancing features help prevent unauthorized access or misuse of sensitive information.
Fairness in Mitigating Harmful Biases: Ensuring fairness in AI systems involves identifying and mitigating biases that can lead to discriminatory outcomes. Fairness promotes equitable treatment of all individuals and groups without favoritism or prejudice. Accountability and Transparency: AI systems should be accountable for their decisions and actions, meaning that it should be clear who is responsible for the system’s performance and outcomes. Transparency ensures the AI’s processes and algorithms are open and understandable to relevant stakeholders.
Valid and Reliable: Validity in AI systems refers to the accuracy and effectiveness of the system in achieving its intended goals. Reliability relates to the consistency and dependability of the AI system in delivering accurate results over time. These characteristics collectively contribute to building trust in AI systems by ensuring they operate ethically, responsibly, and effectively.
GRC’s New Role in AI Risk Management:
Irrespective of involvement in AI system design, development, deployment, or utilization, organizations can leverage frameworks like NIST and ISO guidelines on AI risk management to effectively manage risks and ensure trustworthiness. By integrating these best practices into their GRC functions, organizations can navigate the intricate web of AI risks, shield against potential harms, and cultivate stakeholder trust. As the AI revolution continues to reshape industries and societies, the evolution of the GRC role plays a pivotal part in fostering responsible AI adoption, mitigating risks, and upholding the tenets of trust and accountability in this AI-driven era.
Mastering Tomorrow: Diving into the Realm of Current AI Frameworks:
1. ISO 23894 – Guidelines for the Management of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning ISO 23894 offers a comprehensive set of guidelines specifically tailored to the management of AI and machine learning technologies. By incorporating principles from this standard into their GRC framework, organizations can establish structured processes for identifying, assessing, and mitigating socio-technology risks associated with AI implementation.
Key benefits of leveraging ISO 23894 include:
· Enhanced transparency and accountability in AI decision-making processes.
· Improved risk identification and management through structured controls and monitoring mechanisms.
· Align with best AI governance practices to ensure ethical and responsible AI deployment.
2. ISO 42001 – Asset Management Systems for Socio-Technical Systems ISO 42001 provides a framework for managing assets within socio-technical systems, emphasizing the interplay between technology, human factors, and organizational processes. By integrating ISO 42001 principles into their GRC approach, organizations can develop a holistic understanding of AI socio-technology risks and implement targeted controls to mitigate them.
Benefits of adopting ISO 42001 include:
· Improved asset visibility and control across the organization, facilitating risk assessment and decision-making.
· Enhanced resilience to socio-technology risks by considering the complex interactions between technology and human elements.
· Alignment with international standards to foster trust and confidence among stakeholders.
3. NIST AI RMF – National Institute of Standards and Technology’s Risk Management Framework for AI Systems NIST AI RMF provides a risk management framework specifically tailored to AI systems, guiding organizations in identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with AI technologies. By leveraging NIST AI RMF within their GRC strategy, organizations can streamline the management of AI socio-technology risks and enhance their overall risk posture.
Benefits of adopting NIST AI RMF include:
· Structured risk assessment processes tailored to the unique characteristics of AI systems.
· Clear guidelines for implementing risk controls and monitoring mechanisms in AI environments.
· Align with recognized AI risk management best practices to support compliance and governance objectives.
Conclusion:
As AI continues to permeate all facets of the business landscape, the GRC function must adapt to meet the evolving needs of the AI era. By embracing new roles that encompass AI risk management, trustworthiness evaluation, and ethical oversight, GRC professionals can position themselves as strategic partners in guiding their organizations through the complexities of AI adoption. Through proactive collaboration with data scientists, IT teams, and business leaders, GRC professionals can shape a holistic approach to AI governance that balances innovation with risk awareness, ultimately driving sustainable growth and competitive advantage in an AI-driven world.
What’s next?
🌟 🌟 Elevating AI Development through Compliance Awareness 🌟 🌟
💫I am committed to educating and partnering with businesses and service providers about AI cybersecurity and compliance practices, as well as building a network for a secure AI ecosystem💫
FOLLOW ME & Subscribe to Our Newsletter :
Feel free to connect for insights on enhancing your AI GRC business strategy.
Contact us:
Contact us

